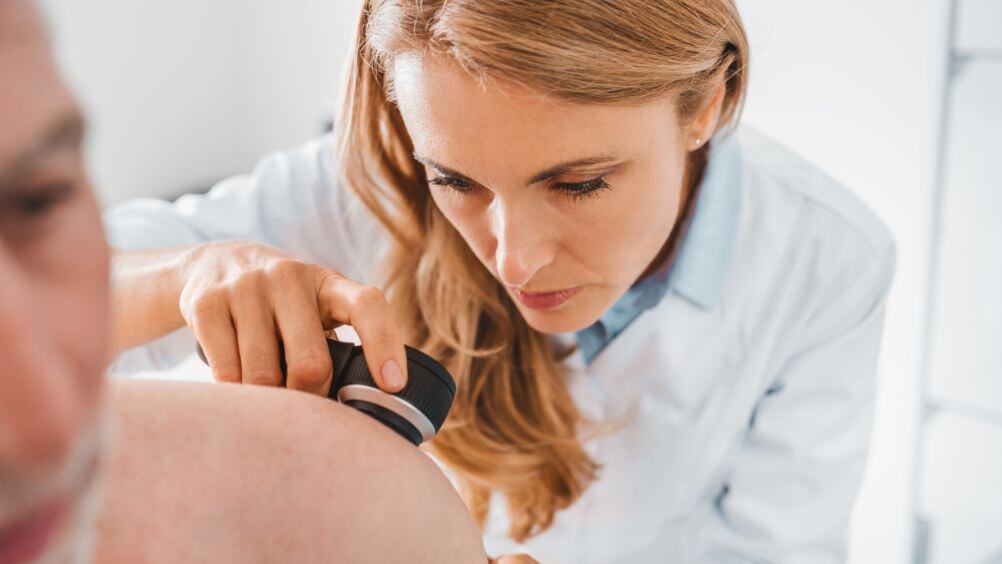
Skin cancer is one of the most common cancers in the United States. While most people know about the issues surrounding sunburns and unprotected exposure to UV rays, many don’t realize that certain skin cancers are more serious than others. Melanoma, for example, can spread quickly to other organs of the body, so it’s essential to have your doctor check any suspicious-looking skin lesions as soon as possible.
Here are some surprising facts about skin cancer you should know in order to protect yourself and make sure you don't unnecessarily expose your skin.
UV Radiation Actually Changes Your DNA
There are several different types of skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), melanoma, and many others. While there are differences between each type of skin cancer, exposure to ultraviolet light leads to DNA damage that can result in any type of skin cancer. Ultraviolet radiation can come from sunlight or artificial lights, like tanning beds. With so many people affected, we must focus on reducing risk and detecting skin cancer early since it is the key to successful treatment.
Skin Cancer Won’t Go Away On Its Own
A skin cancer diagnosis will require treatment. Treatment for skin cancer usually requires surgery. In some cases, patients also need some combination of other cancer treatments such as radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and/or immunotherapy.
The surgery is often performed by a dermatologist. You might assume that everything is fine after having a cancerous spot removed by a dermatologist. However, the other treatments for skin cancer are best delivered by an oncologist – a doctor that specializes in cancer.
Tanning Bed Use Increases the Risk of Melanoma
Routine tanning bed use isn’t associated with increased risks in various skin cancers but is primarily tied to melanoma, which is the deadliest form of skin cancer.
The risks of melanoma are increased by exposure to tanning beds and UV light. While basal cell carcinoma is more common, fewer people in the population routinely use a tanning bed than have exposure to UV light from the sun.
If you like the look of a tan, consider using spray tans or other sunless tanning products. It’s important to remember that sunless tanning products do not contain UV protection, so make sure to continue to use sunscreen and other protective products like hats and sunglasses.
Your Skin Can Be Damaged on Cloudy Days
Sunscreen isn’t just for going to the beach. It is for everyday wear. Whether you’re spending a day at the beach or working a nine-to-five inside of an office, protecting your skin from harmful UV rays is essential. Even if it’s overcast, UV rays can still penetrate clouds, so be sure to reapply sunscreen every few hours (even if you don’t see any sun), and cover up with clothing and hats when possible.
Sunscreen Isn’t Always Enough
While sunscreens play an essential role in protecting your skin from harmful UV rays, they aren’t always enough. Melanomas are often found on parts of your body that have been covered by clothing or sunscreen. So, while sunscreen is critical, don’t rely on it as your only source of protection—use common sense when you’re out in the sun and wear clothes to cover any exposed skin.
It’s also helpful to cover up with a hat or sunglasses to protect your scalp, eyes, and face.
Check out our blog: 4 Apps That Help Detect Skin Changes That May Lead to Skin Cancer
Some Medications Can Cause you to Burn Easier
Certain medications might cause sun sensitivity. Taking these certain medications could put you at an increased risk of developing a burn from UV exposure. This damage can increase your risk of developing skin cancer. Discuss ways to reduce your risk with your doctor. You might want to talk to your doctor about switching from one type of drug to another. Or, if your prescription is only temporary, consider taking it when you’re less likely to be exposed to sunlight—such as in winter months in northern climates or on rainy days in southern regions.
If your medications cannot be changed, it is important to use other forms of skin protection. This includes wearing sunblock every day. You can also wear hats and sunglasses to help reduce direct exposure. Additionally, long-sleeved shirts and pants that help cover exposed skin can reduce the potential of developing a sunburn.
Skin Cancer Appears in Surprising Areas
More than any other part of your body, you’re likely to be diagnosed with skin cancer on your face. Most melanomas occur in areas exposed to ultraviolet light, such as your head, neck, and ears, though you can get them on other parts of your body. These other areas include places that don’t get touched by the sun, like the bottoms of your feet, or areas that are covered by a bathing suit.
Don’t forget about your lips—sunscreen can help prevent skin cancer on your face and other areas, but your lips contain a lot of sensitive tissue that doesn’t get much sun protection.
Be sure to check your entire body for signs of skin cancer regularly. If you notice that anything is abnormal or itches, see a dermatologist. Even skin cancers that are in early stages can be dangerous because they can spread before they are even noticed. An annual exam by a physician is a good idea since you can’t see all of your skin.
Skin Cancer Care Available at Willamette Valley Cancer Institute
If you or a loved one have been recently diagnosed with skin cancer – melanoma or nonmelanoma – schedule an appointment with an oncologist who can review the details of your diagnosis and help you determine if additional treatments are recommended. Our skin cancer specialists are located in the Willamette Valley, including in Corvallis, Eugene, Florence, and Lincoln City, Oregon.