Skin cancer occurs when changes in the DNA of skin cells cause the cells to grow rapidly. This rapid growth creates abnormalities on the skin, such as a mole or bump. While not all skin changes are cancerous, some develop into a type of skin cancer.
There are two main types of skin cancer: melanoma and non-melanoma. Non-melanoma skin cancer is the most common type of skin cancer in the US, and it is usually less serious. Melanoma skin cancer, on the other hand, is usually more serious. Fortunately, there are effective treatment options available for both types of skin cancer.
How is Skin Cancer Diagnosed?
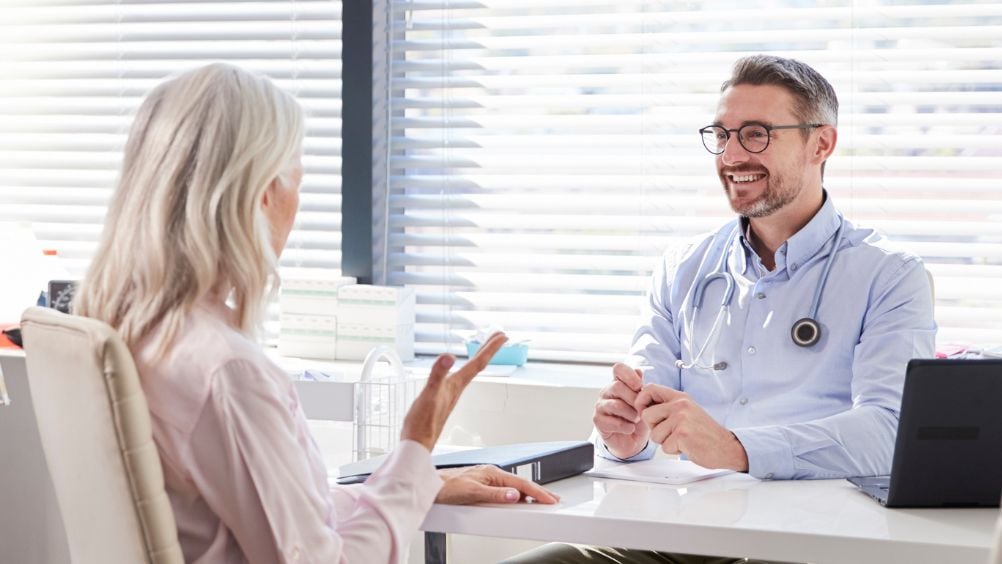
If you notice a new spot on your skin, schedule an appointment with your doctor. The spot may develop slowly, or it could show up almost overnight. And, it doesn’t necessarily appear in areas normally exposed to the sun. Have a dermatologist inspect your skin once a year in addition to tracking any changes on your own.
Related Reading: 4 Apps That Help Detect Skin Changes That May Lead to Skin Cancer
If the dermatologist determines that a spot on your skin shows signs of cancer, they may remove it right away and send it to a pathologist for review. However, if the area is rather large or in an area where scarring is possible, the dermatologist is more likely to perform a biopsy for further testing.
The report provided to the dermatologist indicates whether cancer is present. If it is, the report will also indicate the type – melanoma or non-melanoma.
Understanding Your Skin Cancer Treatment Options
For many patients, surgery is all that’s needed. For those whose skin cancer has grown deep into the skin or progressed to other areas of the body, additional treatments will ensure that all of the cancer cells are destroyed.
The treatment plan for skin cancer depends on various factors, including the type, grade, size, location, and depth of the cancerous skin cells. Additional types of treatment for non-melanoma and melanoma skin cancer include:
- Radiation therapy - external beam or high-dose brachytherapy
- Chemotherapy - applied to the skin or given through an IV
- Immunotherapy - boosting your own immune system to fight the cancer cells
- Targeted therapy - some skin cancers show signs of a genetic mutation causing the cancer cells to grow. Drugs are available to target some of these genetic changes.
Radiation therapy is often combined with surgery because it’s effective and focuses primarily on the area where the cancer was removed. This keeps the side effects to a minimum compared to the more significant side effects of drug therapies.
External Beam Radiation Therapy for Skin Cancer
External beam radiation therapy is commonly used to treat skin cancer. It focuses high-energy beams from a machine called a linear accelerator at the area where the cancer was located, killing any remaining cancer cells in the area. External beam radiation therapy is given five days a week for three to eight weeks.
High-Dose Rate (HDR) Brachytherapy for Skin Cancer
Another method for delivering radiation is called HDR brachytherapy. In this type of radiation treatment, the radiation oncologist will place a device on top of the skin (superficial brachytherapy) so radiation therapy can be delivered directly to the area. The device will emit radiation to kill the skin cancer cells. Brachytherapy offers several benefits, including less damage to surrounding healthy tissue and fewer overall treatments compared to external beam radiation therapy. A treatment course for brachytherapy is typically 2 times a week for about four weeks.
It’s also a good option for those whose cancer is in a sensitive area that could cause disfigurement or extensive scarring, such as the nose, scalp or forehead, and even lips. It’s also helpful for patients who aren’t good candidates for surgery due to their overall health condition.
A Patients Experience with Choosing Brachytherapy for Non-Melanoma Treatment
After being diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma on his nose, this patient chose HDR brachytherapy for non-melanoma skin cancer at Willamette Valley Cancer Institute as an alternative to surgery. The treatment was quick, painless, and allowed for a faster recovery with no activity restrictions.
In this video, he shares his personal story—including how both he and his wife were treated with radiation therapy—and why they trusted the team at Willamette Valley Cancer Institute for their care. Learn more about how brachytherapy for non-melanoma treatment offers an effective, non-invasive option for skin cancer patients.
When is Radiation Therapy Recommended for Skin Cancer?
Radiation can be effective at treating melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer. The following are reasons why your oncologist may suggest radiation therapy:
- Effective against various types of skin cancers, including melanoma and non-melanoma small basal or squamous cell skin cancers
- Stops the growth of advanced forms of skin cancer or those that have spread to other areas
- Effectively treats larger areas on the skin
- Treats areas that are difficult to reach with surgery
- Kills any remaining cancer cells after surgery
- Reduces the likelihood of the cancer returning in that area of the body
- Provides an option for patients who can’t have surgery
What Side Effects Does Radiation Therapy Have?
Radiation therapy is meant to kill cancer cells. However, it can also damage healthy tissue in the nearby area of the body being treated. Because of this, you may experience some side effects.
The most common side effect of radiation is irritation of the skin at the treatment area. This can be like a bad sunburn, sores, or a rash. However, these usually disappear after treatment is finished.
You may also experience fatigue and hair loss in the area of treatment. If radiation is given in the head or neck area, you may also notice dry mouth. Your radiation oncologist will help you understand what to expect and how to manage the side effects.
Importance of Skin Care During Radiation Therapy
To help reduce the side effects of radiation, you need to care for your skin so you can recover as soon as possible. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Clean the treated area with warm water. Gently cleanse with a soft cloth or sponge to avoid further irritation.
- Avoid shaving the treated area.
- Apply moisturizer to the treated area, even if you don’t notice redness or itching.
- Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing. Try to wear soft fabrics that touch your skin.
- Wear sunscreen and avoid sun exposure.
- Avoid using hot tubs.
- Avoid extreme temperatures, such as heating pads or ice packs.
Post-Radiation Care
You should expect follow-up appointments once or twice a year if you received skin cancer treatment from an oncologist. In between appointments, check your skin for any changes and record them, whether in an app or in a hand-written notebook. Make sure to share any concerns or questions during each follow-up appointment. It’s important to maintain proper skin health by avoiding sun exposure, wearing sunscreen, limiting alcohol intake, exercising regularly, and eating a balanced diet.
Related Reading: 4 Practical Tips for Lowering Skin Cancer Risk
Skin Cancer Doctors in the Willamette Valley and the Oregon Coast
Our team of skin cancer experts at Willamette Valley Cancer Institute is available to help if your dermatologist feels that additional treatments would benefit you. We have locations throughout the region, including Albany, Corvallis, Eugene, Florence, Lincoln City, and Newport, Oregon. We also offer second opinions to ensure you receive the best care possible.